
How Long Does It Take to Learn Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is one of the most critical and rapidly growing fields today, offering professionals the opportunity to protect valuable information and prevent cyber threats.
But how long does it take to learn cybersecurity? If you’re considering entering this field, understanding the time commitment required can help set realistic expectations and help you plan your learning journey.
Learning cybersecurity involves mastering a range of skills and concepts, from basic IT knowledge to advanced networking and security principles. For beginners, this might seem daunting, but with the right approach and resources, becoming proficient in cybersecurity is achievable.
This article will explore the essential learning stages, resources, and timelines to give you a clear idea of how long it generally takes to become a cybersecurity professional. It doesn’t matter if you’re learning from home, looking for free resources, or aiming for a structured certification path; this guide will help you navigate the journey.

RELATED: The Impact of Quantum Computing on Cybersecurity
What Does “Learning Cybersecurity” Really Mean?
When we talk about “learning cybersecurity,” it’s important to clarify what this means in practical terms. Cybersecurity is a broad field with various career paths, each requiring different skill sets and levels of expertise.
So, are you aiming to become a generalist, securing foundational knowledge, or are you looking to specialize in a specific role like a Security Operations Center (SOC) Analyst, penetration tester, or even a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)?
The answer to how long it takes to learn cybersecurity varies significantly based on your goals. However, the most common approach is to start with foundational knowledge and gradually build more specialized skills. This is particularly relevant for beginners, who must first develop a strong base in IT and networking before delving deeper into cybersecurity concepts.
For most learners, the goal of “learning cybersecurity” is to acquire a solid foundation in cybersecurity principles, which will prepare them for entry-level roles and further specialization. Just like constructing a building, a strong IT and networking foundation is essential for anyone looking to build expertise in cybersecurity.
With this base, learners can better understand and manage security challenges in real-world scenarios, equipping them with the skills needed to move forward confidently.
SEE MORE: The Future of Cybersecurity in the Age of AI (Artificial Intelligence)
How Long Does It Take to Learn Cybersecurity?
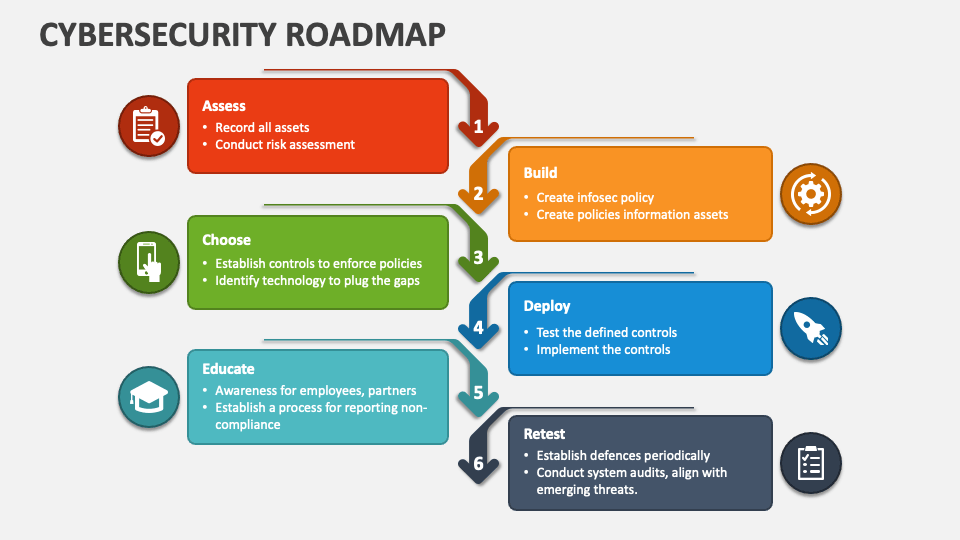
Step 1: Building an IT Foundation
The first step in learning cybersecurity is establishing a strong IT foundation. This stage covers essential knowledge areas, including computer hardware, operating systems, and basic networking. A solid understanding of these fundamentals helps you grasp how different systems work, which is crucial when identifying and managing security vulnerabilities.
For beginners, this step typically takes around 1 to 2 months of dedicated study, especially if working full-time on this learning path. Popular certifications like CompTIA A+ can provide a structured approach to learning IT basics, covering core topics like hardware, troubleshooting, and operating systems.
Step 2: Learning Networking Fundamentals
After mastering IT basics, the next step is networking—a vital component of cybersecurity. Networking skills enable you to understand how systems communicate, manage network infrastructure, and secure data flow across networks. Key networking concepts include IP addressing, subnetting, network design, and network security principles.
Certifications like CompTIA Network+ provide a vendor-neutral framework for learning networking, making them ideal for anyone new to the field. For beginners, a typical timeline to build networking knowledge is around 3 to 6 months, assuming consistent study.
A strong grasp of networking fundamentals prepares you to tackle more complex cybersecurity topics down the line.
Step 3: Diving into Cybersecurity Basics
Once you’ve covered IT and networking, you’re ready to explore the core elements of cybersecurity. This includes understanding security principles, threat management, cryptography, and vulnerability assessments. Beginners often benefit from certifications like CompTIA Security+ or similar online courses, which outline key cybersecurity domains.
Learning cybersecurity basics can take anywhere from 6 months to a year, depending on your study schedule and prior knowledge. This stage provides the foundation necessary for entry-level roles and helps you understand how to respond to and mitigate security threats effectively.
This step-by-step approach ensures that beginners develop a comprehensive understanding of cybersecurity fundamentals, building knowledge progressively. Each step prepares you for the next, creating a clear roadmap to follow.
READ ALSO: Home Wi-Fi Network: A Complete Guide
How Long Does It Take to Learn Cybersecurity for Free?
For those who want to learn cybersecurity without financial investment, there are plenty of free resources available. However, free learning often requires more self-discipline and time than structured, paid programs.
For beginners, a realistic timeline to gain foundational cybersecurity knowledge through free resources is approximately 6 months to a year, especially if studying part-time.
Free Resources for Learning Cybersecurity
- YouTube Channels: Channels like “Professor Messer,” “Cyber Mentor,” and “HackerSploit” offer tutorials on everything from IT basics to ethical hacking.
- Open Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udacity offer introductory cybersecurity courses for free. Some programs provide structured pathways, like IBM’s Cybersecurity Analyst certificate, which can be audited for free.
- Community Resources and Forums: Websites like CyberSecLabs, TryHackMe, and Hack The Box provide free labs and exercises to practice real-world cybersecurity skills. Communities like Reddit’s r/cybersecurity or the InfoSec Discord group are valuable for networking and accessing additional free resources.
Pros and Cons of Free Learning
While free resources are abundant, they come with trade-offs. On the positive side, learning for free allows you to explore different areas of cybersecurity without a financial commitment. However, free resources often lack the structured progression that paid courses provide, making it harder for beginners to understand where to start or which topics to prioritize.
To maximize the benefits of free learning, it’s helpful to create a self-guided roadmap based on recommended certifications like CompTIA Security+ or other foundational programs. This allows you to follow a structured syllabus, even if you’re learning independently.
How Long Does It Take to Learn Cybersecurity from Home?
Learning cybersecurity from home is a popular choice, especially with the flexibility and accessibility of online programs. Remote learning allows you to set your own pace, making it an excellent option for both full-time and part-time learners.
For beginners, the typical timeline to learn cybersecurity from home can range from 6 months to 2 years, depending on your commitment level and prior experience.
Structured Online Programs
Several reputable programs allow learners to gain comprehensive cybersecurity knowledge from home:
- Google Cybersecurity Professional Certificate: Designed for beginners, this program covers key concepts and practical skills in around 6 months, based on a part-time schedule (about 7-10 hours per week).
- Microsoft Cybersecurity Analyst Program: Another flexible, structured course that can take around 6 months with a commitment of 10 hours per week.
These programs offer clear paths and goals, which can reduce the learning timeline compared to self-paced study. Online courses also provide support through quizzes, assessments, and, in some cases, instructor feedback.
Self-Paced vs. Structured Learning
One of the biggest decisions when learning cybersecurity from home is whether to pursue a self-paced approach or a structured program. A structured program with a clear syllabus often leads to faster progress, as it guides you through essential topics in a logical sequence. On the other hand, self-paced learning allows for greater flexibility but requires strong self-motivation and can take longer to complete.
By carefully selecting resources and establishing a study schedule, learning cybersecurity from home is entirely feasible. Whether through structured programs or a self-guided path, home learning makes cybersecurity education accessible to a wide range of learners.
Key Factors Affecting Learning Duration in Cybersecurity
The time it takes to learn cybersecurity can vary widely based on several personal and logistical factors. Here are some of the key aspects that influence the learning timeline:
1. Prior Experience
- Those with a background in IT or networking will have a head start, as they’re already familiar with the foundational concepts. This can reduce the learning time significantly, often by several months. For absolute beginners, however, building this base will take longer as they need to first acquire essential IT and networking knowledge.
2. Learning Style
- Different learning styles affect how quickly someone progresses. Individuals who thrive in structured, classroom-like settings may progress faster in formal online courses, while self-starters may benefit from self-paced learning. Understanding your learning style can help you choose the most effective resources, whether they are hands-on labs, textbooks, video lectures, or interactive courses.
3. Commitment Level
- Time commitment is one of the most critical factors. Cybersecurity can be learned faster if you study full-time, dedicating 20-40 hours per week. For part-time learners putting in 5-10 hours per week, the timeline will naturally extend. Consistency is key, as regular study habits help reinforce complex concepts and reduce the need for frequent review.
4. Resources Used
- The quality and depth of resources impact the speed of learning. Comprehensive certification programs (such as those provided by CompTIA, Cisco, or Google) offer clear guidance and typically speed up learning. Free resources, while valuable, may lack structure and require additional time to find, organize, and apply.
Summary of Typical Timelines
- For complete beginners: 6 months to 2 years based on part-time vs. full-time study.
- For those with some IT/networking experience: 3-12 months, depending on focus and consistency.
Understanding these factors allows you to set realistic expectations and create a plan that aligns with your current knowledge, lifestyle, and resources.
Certifications and Their Impact on the Learning Timeline
Certifications play a crucial role in cybersecurity, not only by structuring the learning journey but also by providing a valuable credential that demonstrates your expertise to potential employers. Using certifications as milestones can streamline the learning process and give you clear goals to work toward.
Recommended Certifications for Beginners
- CompTIA A+ and Network+: These certifications cover foundational IT and networking skills, which are essential for cybersecurity. They’re ideal for complete beginners, with a typical timeline of 3-6 months for each certification, depending on prior knowledge.
- CompTIA Security+: This entry-level cybersecurity certification is highly regarded and offers a comprehensive introduction to security concepts, threat management, and risk mitigation. For those with no prior experience, Security+ usually requires 4-6 months of study.
- Google Cybersecurity Professional Certificate and Microsoft Cybersecurity Analyst Program: These vendor-neutral, online certifications can be completed in around 6 months with a part-time schedule and cover foundational cybersecurity skills in a structured format.
Benefits of Certification in Cybersecurity
- Structured Learning Path: Certifications provide a structured syllabus that guides you through necessary topics in a logical order, making it easier to progress without missing important concepts.
- Resume Boost: Many entry-level cybersecurity roles list certifications as a job requirement or a strong preference, so holding certifications can significantly improve your job prospects.
- Career Progression: Certifications like Security+, and later, more advanced ones such as CISSP or CEH, validate your skills and help you move toward specialized roles.
Completing certifications can fast-track your cybersecurity education by giving you a roadmap to follow. For beginners, earning certifications not only builds confidence but also signals commitment and competence to future employers.
The Continuous Learning Aspect of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is a constantly evolving field, with new threats, technologies, and regulations emerging regularly. This means that even after you’ve built a foundational knowledge base, continuous learning is essential to stay relevant and effective in your role.
Why Continuous Learning is Essential
- New Threats and Vulnerabilities: Cyber threats constantly adapt, and new vulnerabilities emerge as technology evolves. Professionals need to stay updated on these changes to effectively defend against the latest attack vectors.
- Advanced Certifications: Once foundational certifications are complete, more advanced certifications like Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH), or Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP) allow you to specialize and deepen your expertise.
- Specializations: Cybersecurity encompasses various domains, such as cloud security, ethical hacking, and incident response. As you gain experience, you may choose to focus on a specific area, which will require ongoing training and possibly additional certifications.
Staying Updated and Expanding Skills
- Regular Training and Courses: Many cybersecurity professionals take regular courses on platforms like Cybrary, Udacity, and LinkedIn Learning to learn about the latest tools and techniques.
- Industry Resources and Communities: Participating in cybersecurity communities, such as InfoSec Twitter, Reddit’s r/cybersecurity, and cybersecurity conferences, helps professionals stay informed and network with others in the field.
- Hands-On Practice and Labs: Platforms like Hack The Box, TryHackMe, and CyberSecLabs offer labs where professionals can simulate real-world attacks and defenses, allowing them to practice advanced skills and new techniques.
Continuous learning is an integral part of a successful cybersecurity career, keeping you adaptable and effective in an industry that never stands still.
Practical Tips for Accelerating Your Cybersecurity Learning
For those eager to reduce the time it takes to learn cybersecurity, adopting certain study strategies can make a significant difference. Here are some practical tips to help you learn faster and more effectively:
1. Set Up a Dedicated Study Schedule
- Consistency is crucial in mastering cybersecurity concepts. Establish a regular study routine and set specific goals for each week, whether you’re working through an online course or studying for a certification.
- Aim for at least an hour of focused study each day or block out dedicated time each weekend if balancing work or school.
2. Combine Theory with Hands-On Practice
- Cybersecurity is a skill-based field where hands-on experience is as essential as theoretical knowledge. Use platforms like Hack The Box, TryHackMe, or even virtual labs that accompany certifications to apply what you learn in real-world scenarios.
- Setting up your own virtual lab environment using VirtualBox or VMware is another cost-effective way to gain practical experience.
3. Join Online Communities and Forums
- Cybersecurity communities, such as Reddit’s r/cybersecurity, Discord groups, or LinkedIn, are excellent for learning from others, sharing resources, and staying motivated.
- Participate in discussions, ask questions, and take advantage of the shared knowledge of professionals and other learners in these communities.
4. Build a Portfolio of Cybersecurity Projects
- Showcase your skills by building a portfolio of projects, like vulnerability assessments, network security setups, or small penetration testing assignments. A portfolio not only reinforces your learning but also adds credibility when applying for jobs.
- Document your work on GitHub or a personal blog to track your progress and demonstrate your capabilities to potential employers.
5. Leverage Learning Tools and Resources
- To stay organized and efficient, consider using note-taking tools like Notion or OneNote to track your study notes, resources, and goals. This helps you review and retain information more effectively.
- Use flashcards for memorizing essential terms and concepts, especially for certification exams, with tools like Anki or Quizlet.
By applying these strategies, you can make your cybersecurity learning journey smoother and more efficient, potentially reducing the overall time it takes to gain the skills you need.
Conclusion
Learning cybersecurity is a rewarding yet challenging journey that requires time, dedication, and a structured approach. For beginners, the typical timeline can range from 6 months to 2 years, depending on factors like prior knowledge, study commitment, and the resources used.
While there are numerous free and paid resources available, a step-by-step approach, starting with IT basics, followed by networking, and then diving into cybersecurity principles, provides the most effective path to gaining competency in this field.
For those learning from home or exploring free resources, self-discipline, and a well-structured plan are essential. Certifications like CompTIA Security+ and Network+ can provide invaluable guidance and help open doors to entry-level roles.
Additionally, continuous learning is critical, as cybersecurity is a constantly evolving field with new threats and technologies emerging regularly.
Ultimately, cybersecurity offers a fulfilling career for those willing to invest the time and effort. Whether you’re aiming to start with the basics or specialize in advanced areas, the resources and strategies outlined in this article provide a clear roadmap for success in your cybersecurity journey.
FAQ
How hard is it to learn cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity can be challenging to learn, especially for those new to IT and networking, as it requires understanding complex concepts in technology, security protocols, and threat analysis. However, with dedication, the right resources, and a structured learning path, it’s manageable for beginners.
Starting with foundational IT and networking knowledge before moving into specialized cybersecurity topics makes the learning process more accessible and less overwhelming. Hands-on practice through labs and simulations also helps reinforce theoretical knowledge, making the learning curve easier over time.
How long does it take to study cybersecurity?
The time needed to study cybersecurity varies widely depending on individual goals, prior experience, and the amount of time dedicated each week. For complete beginners, it usually takes between 6 months and 2 years to gain enough proficiency for entry-level positions, with a focused learning path that includes IT fundamentals, networking, and core cybersecurity principles.
Those with prior IT knowledge may require less time, often around 3-12 months with consistent study. Learning continuously beyond this point is essential, as cybersecurity is a dynamic field that demands ongoing skills development.
How long did it take to learn cybersecurity?
This is subjective and can depend on the learner’s background and study approach. For example, individuals who committed to intensive study, such as those completing bootcamps or immersive courses, have reached an entry-level understanding within 6-12 months. Others who took a part-time approach while working or studying might have taken closer to 1-2 years to feel proficient in core cybersecurity skills. The timeline ultimately varies, but most learners who follow a structured path report significant progress within the first year.
Can I learn cybersecurity in 2 months?
Learning cybersecurity in just two months is possible but very challenging, especially for complete beginners. In this short timeframe, you can build a foundational understanding by focusing on the basics of IT, networking, and introductory security concepts.
However, achieving job-ready skills or preparing for certifications typically requires more time. If you have prior experience in IT or a related field, you might be able to accelerate your learning in two months, but for those starting from scratch, two months is generally not enough for comprehensive cybersecurity training.
Transform your career with ExcelMindCyber’s roadmap to six-figure success in cybersecurity. Our program delivers essential guidance and strategies to help you master the skills and secure the roles that matter. Start today and take the first step towards transforming your career!
