
How to Become a GRC Analyst?
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) have become critical pillars for businesses striving to maintain integrity, minimize risks, and navigate complex regulatory systems. Among the professionals leading this charge are GRC Analysts, key players responsible for safeguarding organizations from legal and financial pitfalls.
Whether you’re a newcomer exploring how to become a GRC Analyst or a professional seeking to pivot into this field, this guide provides a step-by-step approach to building a successful career.
With increasing demand across industries such as finance, healthcare, technology, and energy, the GRC Analyst career path offers lucrative opportunities for growth and impact. In this article, we’ll critically examine the role of a GRC Analyst, the essential skills needed, and actionable steps to break into this dynamic profession, even with no experience.

How to Become a GRC Analyst: Summary Table
| Aspect | Details |
| GRC Analyst Salary | Entry-Level: $34,000–$60,000- Mid-Level: $70,000–$120,000- Senior Roles: $200,000+ |
| Career Path | 1. Entry-Level: Compliance Associate, Junior Risk Analyst 2. Mid-Level: GRC Specialist, Policy Officer 3. Advanced: GRC Manager, Chief Risk Officer |
| What You Need | Transferable skills: problem-solving, communication- Education: Business, cybersecurity, or law degree (optional)- Certifications: CISA, CRISC, GRCP |
| How to Start with No Experience | Highlight transferable skills- Volunteer or intern in compliance or auditing- Take foundational GRC courses online |
| How Long It Takes to Learn | Basic Knowledge: 2–3 months- Certification Prep: 4–6 months- Proficiency: 1–2 years with practical experience |
| Top Certifications | CISA (Certified Information Systems Auditor)- CRISC (Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control)- CompTIA Security+ |
| Where to Find Jobs | Job boards: LinkedIn, Indeed, CyberSN- Networking: ISACA, industry conferences- Social media branding |
| Best Resources | Platforms: Lightforth, Coursera, Udemy, ISACA- Certifications: CISA, CRISC, GRCP- Tools: MetricStream, RSA Archer |

RELATED ARTICLE: Can You Learn Cybersecurity on Your Own
What is a GRC Analyst?
A GRC Analyst is a professional who ensures that an organization complies with relevant regulations, manages risks effectively, and maintains strong governance practices. These analysts serve as the backbone of an organization’s compliance and risk management efforts, playing a crucial role in protecting businesses from legal, financial, and reputational harm.
Primary Responsibilities
GRC Analysts tackle a wide range of tasks, including:
- Risk Assessment: Identifying and evaluating potential risks to organizational operations, systems, and processes.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring that the organization adheres to local, national, and international laws and standards.
- Policy Development: Creating, updating, and enforcing internal policies that align with regulatory requirements.
- Auditing and Monitoring: Conducting audits to assess compliance, uncover vulnerabilities, and recommend improvements.
Key Industries for GRC Analysts
The demand for GRC Analysts spans various sectors, such as:
- Finance: Addressing regulatory standards like Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) and Basel III.
- Healthcare: Ensuring compliance with laws like HIPAA for patient data protection.
- Technology: Managing cybersecurity risks and adhering to frameworks like GDPR.
- Energy: Navigating regulations such as NERC standards.
Why Choose a Career as a GRC Analyst?
Pursuing a career as a GRC Analyst can be incredibly rewarding, both professionally and financially. It offers the opportunity to make a tangible impact on an organization’s stability, reputation, and long-term success. Here’s why this career path stands out:
1. High Demand Across Industries
GRC Analysts are in high demand as businesses navigate increasingly complex regulatory landscapes. Industries like healthcare, finance, technology, and energy are actively hiring GRC professionals to address their growing compliance and risk management needs.
The surge in regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS has amplified this demand, making GRC a stable and future-proof career choice.
2. Lucrative Salary Potential
The financial rewards in the GRC field are substantial. The GRC Analyst salary ranges from $34,000 to over $212,000 annually in the U.S., with the average salary around $97,000. This range can increase significantly with experience, certifications, and specialization. Bonuses, stock options, and other incentives can further enhance total compensation.
3. Opportunities for Growth and Specialization
A GRC Analyst career path is diverse, offering numerous opportunities for specialization. Whether you’re interested in data privacy, cybersecurity compliance, or risk management, the field allows you to focus on areas that align with your strengths and interests. This versatility also opens doors to leadership roles, such as GRC Manager or Chief Risk Officer.
4. Real-World Impact
GRC Analysts play a pivotal role in preventing corporate scandals, safeguarding sensitive information, and ensuring ethical business practices. Their work not only shields organizations from financial penalties but also fosters trust among stakeholders, customers, and the public.
5. Accessibility for Career Changers
One of the most appealing aspects of this career is its accessibility. Many professionals successfully transition into GRC roles without prior experience, leveraging transferable skills such as problem-solving, attention to detail, and effective communication.
Additionally, you can start with entry-level positions and grow your career through hands-on experience and targeted learning.
A career as a GRC Analyst offers a combination of financial stability, personal fulfillment, and professional growth, making it an attractive option for those interested in governance, risk, and compliance.
The GRC Analyst Career Path
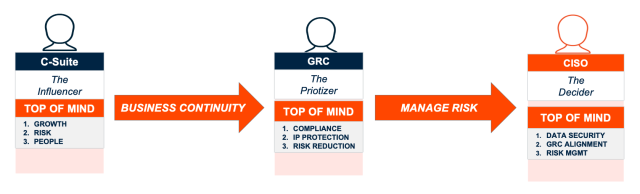
A career as a GRC Analyst offers a structured yet flexible progression, with opportunities to advance into specialized and leadership roles. Whether you’re starting with no experience or transitioning from another field, the GRC Analyst career path is accessible and rewarding.
1. Entry-Level Opportunities
Most professionals begin their journey in GRC Analyst entry-level roles, such as:
- Compliance Assistant: Supporting the implementation of compliance programs.
- Junior Risk Analyst: Assisting in identifying and documenting risks.
- Audit Coordinator: Handling audits and preparing reports under supervision.
Entry-level positions provide exposure to foundational aspects of governance, risk, and compliance, while helping candidates build relevant skills.
2. Mid-Level Roles
With experience and a deeper understanding of GRC practices, professionals can transition into mid-level roles, such as:
- GRC Specialist: Focusing on specific areas like cybersecurity compliance or data privacy.
- Senior Risk Analyst: Leading risk assessment projects and developing mitigation strategies.
- Policy and Compliance Officer: Overseeing the creation and enforcement of company policies.
Mid-level positions often involve greater responsibility, including mentoring junior staff and managing cross-functional projects.
3. Advanced and Leadership Positions
For those with significant experience and expertise, advanced roles offer opportunities to lead and shape organizational strategies:
- GRC Manager: Directing GRC programs and ensuring company-wide compliance.
- Chief Risk Officer (CRO): Defining and managing the overall risk strategy of an organization.
- Director of Compliance: Leading compliance efforts and engaging with regulatory bodies.
Leadership roles typically require strong managerial skills, advanced certifications, and a track record of successful projects.
4. Specialization Options
The GRC field is vast, allowing professionals to specialize in areas that align with their interests and strengths, such as:
- Cybersecurity Compliance: Ensuring adherence to IT security frameworks like ISO 27001 and NIST.
- Data Privacy: Managing regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Financial Risk Management: Navigating banking regulations and market risks.
Specialization not only increases earning potential but also makes professionals more competitive in the job market.
5. Continuous Learning and Growth
The GRC Analyst career path emphasizes lifelong learning. With evolving regulations and emerging risks, staying current through certifications, courses, and professional development is essential for long-term success.
From GRC Analyst entry-level roles to executive positions, this career path provides a blend of stability, growth, and the chance to make a significant impact on organizations.
READ MORE: Can You Get a Job with Google Cybersecurity Certificate? Find Out How
How to Become a GRC Analyst
Embarking on the journey to become a GRC Analyst may seem daunting, especially if you’re starting with little to no experience. However, with the right approach and resources, you can build a strong foundation and launch a successful career in governance, risk, and compliance. Here’s a detailed guide on how to navigate this process.
1. Getting Started: How to Become a GRC Analyst with No Experience
Breaking into the field without experience requires leveraging transferable skills and taking strategic steps:
- Highlight Transferable Skills: Skills such as problem-solving, communication, and attention to detail are highly valued in GRC roles.
- Gain Foundational Knowledge: Start learning about key compliance frameworks, risk management principles, and industry-specific regulations.
- Volunteer or Intern: Look for opportunities in related fields like auditing, legal compliance, or risk assessment to gain hands-on experience.
- Build a Portfolio: Document your learning journey by sharing insights, case studies, or certifications on platforms like LinkedIn to showcase your interest and knowledge.
2. Educational Pathways
While there is no fixed degree requirement for GRC Analysts, certain academic backgrounds can provide a competitive edge:
- Relevant Degrees: Pursue degrees in business administration, cybersecurity, finance, or law to gain foundational knowledge.
- Specialized Courses: Enroll in GRC Analyst courses that focus on governance, compliance frameworks, and risk management. Popular platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and Skillsoft offer comprehensive training.
3. Building Essential Skills
Developing the right skills is critical to excelling in GRC roles:
- Analytical Thinking: Hone your ability to evaluate complex situations and devise effective solutions.
- Technical Knowledge: Familiarize yourself with IT frameworks, cybersecurity fundamentals, and data privacy laws.
- Communication Skills: Practice explaining technical concepts in clear and actionable terms to various stakeholders.
4. Certifications to Advance Your Career
Earning a GRC Analyst certification can significantly enhance your credentials and increase job opportunities:
- CompTIA Security+: A great starting point for building knowledge in IT security.
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA): Focuses on auditing, control, and governance.
- Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC): Ideal for risk management and IT compliance.
- GRC Professional (GRCP): Offers a deep dive into GRC principles and practices.
These certifications validate your expertise and commitment to the field, making you more attractive to employers.
SEE ALSO: Cybersecurity vs Devops Salary: Everything You Need to Know
GRC Analyst Salary and Job Market
Understanding the earning potential and job prospects in the GRC field is essential for anyone considering this career. The role of a GRC Analyst not only offers financial stability but also provides significant opportunities for advancement in a variety of industries.
1. Salary Insights
The GRC Analyst salary can vary widely depending on factors such as experience, location, and industry specialization:
- Entry-Level Salaries: GRC Analysts starting out can expect to earn between $34,000 and $60,000 annually, with variations depending on geographic location and company size.
- Mid-Level Salaries: Professionals with 3–5 years of experience typically earn between $70,000 and $120,000.
- Advanced Roles: Senior positions like GRC Manager or Chief Risk Officer can command salaries exceeding $200,000, particularly in industries like finance and technology.
Other forms of compensation, such as bonuses, stock options, and additional benefits—often supplement these salaries, making the career even more lucrative.
2. Job Market Trends
The demand for GRC Analyst jobs is on the rise due to increasing regulatory pressures and the need for effective risk management. Key trends include:
- Growth Across Industries: Sectors such as healthcare, finance, technology, and energy are actively hiring GRC Analysts to address compliance and risk management needs.
- Remote Work Opportunities: Many GRC roles now offer remote or hybrid working options, expanding accessibility for job seekers.
- Specialized Roles: As the field evolves, new positions focusing on cybersecurity compliance, data privacy, and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) factors are emerging.
3. Where to Find GRC Analyst Jobs
The best platforms for finding GRC Analyst roles include:
- Job Boards: Sites like LinkedIn, Indeed, and Glassdoor frequently feature listings for GRC positions.
- Specialized Platforms: CyberSN and other niche platforms cater to cybersecurity and compliance professionals.
- Networking: Building connections through professional organizations like ISACA or attending industry conferences can help uncover hidden job opportunities.
- Social Media Branding: Actively sharing insights and showcasing expertise on platforms like LinkedIn can attract recruiters and hiring managers.
The combination of competitive salaries and a robust job market makes the GRC field an excellent choice for those seeking a stable and rewarding career. With the right skills and certifications, you can tap into a growing industry that values its professionals.
READ: Is Cybersecurity Hard to Learn? A Complete Analysis
GRC Analyst Entry-Level Opportunities
Breaking into the field as a GRC Analyst at the entry level is an attainable goal, even for those with limited experience. Entry-level roles provide a foundation for learning and growth while offering a pathway to long-term career success.
1. Types of Entry-Level GRC Analyst Jobs
Common GRC Analyst entry-level positions include:
- Compliance Associate: Assisting in the development and implementation of compliance programs.
- Junior Risk Analyst: Supporting risk identification and documentation efforts.
- Audit Assistant: Preparing and organizing materials for internal and external audits.
- Policy Analyst: Reviewing and updating organizational policies to align with regulations.
These roles allow candidates to gain hands-on experience with GRC processes and tools.
2. Skills and Qualifications for Entry-Level Roles
To secure an entry-level GRC Analyst position, focus on these key qualifications:
- Transferable Skills: Highlight abilities like problem-solving, attention to detail, and strong communication.
- Foundational Knowledge: Familiarity with compliance standards (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) and risk management concepts.
- Education: Degrees in business, law, finance, or cybersecurity can provide a competitive edge but are not always required.
- Certifications: Entry-level certifications such as CompTIA Security+ or GRC Professional (GRCP) can demonstrate your commitment to the field.
3. How to Stand Out as a Candidate
For aspiring GRC Analysts with no experience, taking proactive steps can make you more competitive:
- Internships and Volunteer Roles: Gain practical exposure by working in related fields, such as auditing or IT support.
- Networking: Connect with professionals on LinkedIn or join groups like ISACA to learn about job openings and trends.
- Showcase Your Learning: Share insights from courses, certifications, or case studies on platforms like LinkedIn to build a visible professional presence.
4. Examples of Entry-Level GRC Analyst Roles
- Risk Analyst Intern at a Financial Institution: Assisting in the identification of financial risks and mitigation strategies.
- Compliance Assistant in a Healthcare Organization: Supporting the implementation of HIPAA compliance measures.
- Junior GRC Analyst in a Tech Firm: Collaborating with IT teams to ensure adherence to cybersecurity frameworks like ISO 27001.
Entry-level roles are stepping stones into the GRC field, offering invaluable experience and the opportunity to develop specialized skills. With the right approach and determination, you can successfully launch your career in this high-demand area.
Challenges and Opportunities in the GRC Field
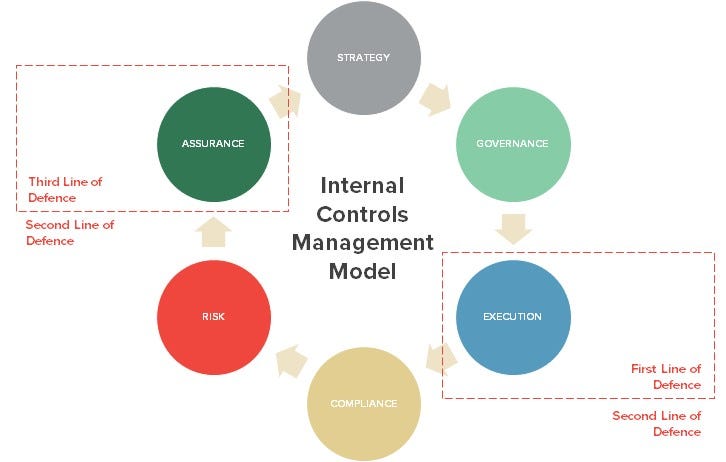
The role of a GRC Analyst is dynamic and rewarding, but it comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding these challenges and the opportunities for growth can help professionals navigate the field successfully.
1. Common Challenges
GRC Analysts face several hurdles due to the evolving nature of regulations, organizational structures, and emerging risks:
- Regulatory Complexity
- The continuous introduction of new laws and frameworks, such as GDPR or CCPA, requires GRC Analysts to stay updated and adapt swiftly.
- Navigating industry-specific regulations (e.g., healthcare’s HIPAA or finance’s SOX) adds another layer of complexity.
- Data Management
- Handling vast amounts of sensitive data while ensuring compliance with privacy laws is a daunting task.
- Implementing robust data protection and cybersecurity measures can be resource-intensive.
- Cultural Resistance
- Some employees may view compliance measures as bureaucratic, leading to pushback during policy implementation.
- Fostering a compliance-friendly culture requires effective communication and change management.
- Emerging Risks
- The rapid advancement of technology, such as artificial intelligence and cloud computing, introduces new vulnerabilities.
- GRC Analysts must anticipate these risks and proactively devise mitigation strategies.
- Resource Constraints
- Limited budgets and staffing can hinder the execution of comprehensive GRC programs, especially in smaller organizations.
- Analysts often need to prioritize tasks and optimize resources for maximum impact.
2. Opportunities for Growth
Despite these challenges, the GRC field offers abundant opportunities for career advancement and specialization:
- Specialization in High-Demand Areas
- Cybersecurity compliance, data privacy, and ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) compliance are emerging as lucrative niches within the GRC space.
- Specializing in these areas can lead to higher earning potential and increased job security.
- Leadership Roles
- With experience, GRC Analysts can progress to leadership positions, such as GRC Manager, Chief Risk Officer, or Director of Compliance.
- These roles involve shaping organizational strategies and managing cross-departmental teams.
- Global Demand
- As businesses expand internationally, the demand for GRC professionals familiar with global regulations continues to rise.
- Analysts with knowledge of international frameworks like GDPR or NERC standards have a competitive edge.
- Continuous Learning and Certification
- Pursuing advanced certifications and participating in professional development programs allows GRC professionals to stay ahead of industry trends.
- Lifelong learning ensures career longevity and relevance in a rapidly changing industry.
ALSO SEE: How to Start a Cybersecurity Firm
How to Succeed as a GRC Analyst

Succeeding as a Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) Analyst requires more than technical knowledge and regulatory expertise. It demands a proactive approach to career development, effective communication, and a commitment to continuous learning. Here’s how to stand out and excel in the field.
1. Networking and Building Relationships
- Professional Organizations: Join industry groups like ISACA or attend GRC-focused events and seminars to connect with peers and mentors.
- Social Media Presence: Actively share insights, articles, or certifications on LinkedIn to establish yourself as a knowledgeable professional.
- Mentorship: Seek guidance from experienced GRC practitioners who can offer career advice and introduce you to opportunities.
2. Lifelong Learning and Staying Updated
- Certifications: Regularly pursue relevant credentials such as Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA) or Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC).
- Workshops and Webinars: Attend events that focus on emerging risks, regulatory changes, and best practices in GRC.
- Industry News: Subscribe to reputable publications and blogs to stay informed about changes in laws and industry trends.
3. Developing Core Skills
To excel as a GRC Analyst, focus on honing these essential skills:
- Analytical Thinking: Cultivate the ability to assess risks and devise practical mitigation strategies.
- Communication: Learn to articulate complex compliance concepts clearly to stakeholders across all levels.
- Technical Proficiency: Understand IT frameworks and tools used in cybersecurity and risk management.
4. Specialize in a Niche
- Cybersecurity Compliance: Focus on frameworks like ISO 27001 or NIST if you have a technical inclination.
- Data Privacy: Become an expert in regulations like GDPR or HIPAA to cater to industries prioritizing privacy.
- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG): Position yourself in this emerging field by understanding sustainability and ethical practices.
5. Demonstrate Value to Your Organization
- Problem-Solving Initiatives: Proactively identify potential risks and propose effective solutions.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Work closely with legal, IT, and operations teams to embed GRC principles across the organization.
- Metrics-Driven Results: Use measurable outcomes to showcase the impact of your work on risk reduction and compliance improvement.
6. Leverage Technology
- GRC Tools: Familiarize yourself with software like MetricStream or RSA Archer, which streamline compliance and risk management tasks.
- Data Analytics: Use data to identify trends and improve decision-making in GRC processes.
MORE: Cybersecurity Salary: A Comprehensive Guide
Resources for Aspiring GRC Analysts
Embarking on a journey to become a GRC Analyst requires access to the right tools, knowledge sources, and community support. Here’s a curated list of resources to help you build a strong foundation and accelerate your career in governance, risk, and compliance.
1. Recommended GRC Analyst Courses
Structured learning programs can provide the expertise needed to succeed in the GRC field:
- Coursera and edX: Platforms offering courses like “Introduction to Governance, Risk, and Compliance” or “Cybersecurity Compliance Frameworks.”
- Udemy: Practical, affordable courses such as “Complete GRC Foundations” or “Risk Management for Beginners.”
- ISACA Training: Focused programs for certifications like CISA and CRISC, tailored to industry standards.
- Skillsoft: Offers a range of compliance and risk management courses for both beginners and advanced learners.
2. Certifications and Exam Prep Resources
Certifications are key to advancing in the field. Use these resources to prepare:
- Official Certification Guides: Study materials for CISA, CRISC, and CompTIA Security+.
- Practice Exams: Websites like Boson and ExamSnap provide mock tests and simulations.
- Certification Communities: Join forums and groups where certified professionals share tips and resources.
3. Books and Publications
Deepen your understanding of GRC principles and practices:
- Books:
- “Governance, Risk, and Compliance Handbook” by Anthony Tarantino.
- “Risk Management Framework” by James Broad.
- Industry Publications:
- GRC Today for the latest trends.
- ISACA Journal for expert insights and case studies.
4. Online Communities and Networking Groups
Connect with peers, mentors, and professionals:
- LinkedIn Groups: Communities like “GRC Professionals Network” and “Cybersecurity Compliance and Risk Management.”
- Reddit Forums: Subreddits such as r/CyberSecurity and r/RiskManagement for discussions and advice.
- Professional Organizations:
- ISACA: Offers events, certifications, and networking opportunities.
- GARP (Global Association of Risk Professionals): Focuses on financial risk and compliance.
5. Free Learning Resources
Explore these no-cost options to kickstart your learning:
- YouTube Channels: Educational content from channels like Cyber Risk Academy and Simply Cyber.
- Blogs and Websites:
- The Open Compliance and Ethics Group (OCEG) for free GRC guides.
- Cybersecurity blogs that cover compliance topics, such as Krebs on Security.
6. Tools and Software
Familiarity with GRC tools can set you apart:
- MetricStream: Widely used for enterprise GRC management.
- RSA Archer: A popular tool for risk management and compliance.
- Compliance.ai: Focuses on tracking and managing regulatory changes.
Conclusion
The journey to becoming a GRC Analyst is both rewarding and impactful, offering opportunities to play a vital role in an organization’s success. By safeguarding businesses from regulatory, financial, and reputational risks, GRC Analysts are at the forefront of fostering ethical practices and ensuring compliance in an ever-evolving landscape.
Now is the perfect time to take the first step toward a fulfilling career in governance, risk, and compliance. Whether you start with an online course, pursue a certification, or connect with industry professionals, each effort brings you closer to your goal. Begin building your knowledge, honing your skills, and exploring GRC Analyst jobs today.
FAQ
What do you need to be a GRC Analyst?
To become a GRC Analyst, you typically need a combination of the following:
Education: While a formal degree isn’t always required, degrees in business, finance, law, cybersecurity, or IT can provide a strong foundation.
Skills: Key skills include analytical thinking, attention to detail, effective communication, and adaptability. Technical knowledge in frameworks like ISO 27001 or GDPR is also beneficial.
Certifications: Credentials such as CompTIA Security+, Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA), or GRC Professional (GRCP) can validate your expertise and make you more competitive.
Experience: Entry-level roles or internships in compliance, risk management, or auditing can provide the practical exposure needed to break into the field.
How long does it take to learn GRC?
The time required to learn GRC depends on your background and the depth of knowledge you want to achieve:
Basic Knowledge: Gaining foundational understanding through self-study or introductory courses can take as little as 2–3 months.
Certifications: Preparing for certifications like CISA or CRISC can take 4–6 months of dedicated study.
Professional Proficiency: Developing a strong command of GRC principles and gaining practical experience through entry-level roles or internships typically takes 1–2 years. Continuous learning is vital, as GRC professionals must stay updated on evolving regulations and industry trends.
How to get GRC certification?
Earning a GRC certification involves the following steps:
Choose a Certification: Identify the most relevant certification for your goals, such as CompTIA Security+, CISA, or CRISC.
Meet Eligibility Requirements: Some certifications, like CISA, require prior experience or specific educational qualifications, while others, like GRCP, have minimal prerequisites.
Study and Prepare: Enroll in a prep course, use official study guides, and take practice exams to build your knowledge.
Register for the Exam: Apply through the certification provider’s official website (e.g., ISACA or (ISC)²) and schedule your exam.
Pass the Exam: Exams typically test your understanding of GRC concepts, frameworks, and best practices.
Maintain the Certification: Some certifications require continuing education credits to stay valid, ensuring you stay updated with industry developments.
Does GRC pay well?
GRC roles are known for their lucrative salaries. Here’s a breakdown:
Entry-Level Roles: Salaries range from $34,000 to $60,000 annually, depending on location and industry.
Mid-Level Positions: Professionals with 3–5 years of experience typically earn between $70,000 and $120,000.
Senior Roles: Advanced positions, such as GRC Manager or Chief Risk Officer, can pay over $200,000 annually. Additional compensation like bonuses, stock options, and benefits often supplement these salaries, making GRC a financially rewarding career.
Transform your career with ExcelMindCyber’s roadmap to six-figure success in cybersecurity. Our program delivers essential guidance and strategies to help you master the skills and secure the roles that matter. Start today and take the first step towards transforming your career!
